Gyro Sensor

EV3 Gyro sensor is more compact and portable than the sensors contained in the Spike Prime or Robot Inventor hub
The 3-axis Gyro in the Spike Prime hub is powerful, but some projects would only work with a more compact and portable sensor.
With QikEasy Adapter and an existing compact EV3 Gyro sensor, you now have a handy gyro available when you require such capability.
How to use it on Spike Prime or Robot Inventor?
- Connect your EV3 Gyro Sensor to the bigger socket on the QikEasy Adapter.
- Connect one end of a Spike Prime cable to the smaller socket on the QikEasy Adapter.
- Connect the other end of the Spike Prime cable to one of the 6 ports on the Spike Prime (or Robot Inventor) hub.
- Your Spike Prime or Mindstorms Hub will detect your EV3 Gyro Sensor through the QikEasy Adapter as a Spike Prime Distance (Ultrasonic) Sensor.
Main Axis Angle & Rotation Rate:
QikEasy Adapter enables your existing EV3 Gyro Sensor to appear as a Spike Prime Distance Sensor to the Spike Prime hub. The main axis angle and rotation rate are encoded into the returned distance data. This data value ranges from 0 to 200. We managed by encode both angle and rate into a single data value by alternating between them during data streaming. When data value is between 0 and 99, it represents Rate. When data value is between 100 and 200, it represents angle. Below are the formulas for decoding these data readings:
When SensorValue < 100:
Angle = SensorValue * 3.6 (calculated result would be in the range of 0 to 360)
When SensorValue >= 100:
Rate = SensorValue – 150 (calculated result would be in the range of -50 to 50)
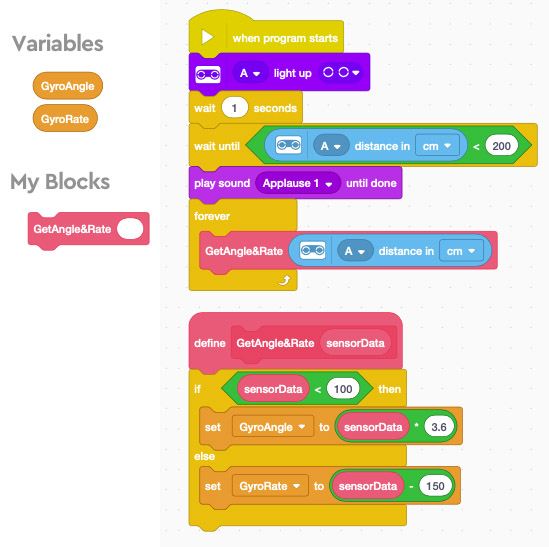
The following example program shows how one would retrieve these readings in Word Blocks. When this program is run, it will set the variables GyroAngle (ranged from 0 to 360) and GyroRate (ranged from -50 to 50) to the angular position and rotation rate of the gyro in real time.
Notes:
- The EV3 Gyro sensor recalibrates itself and reset its zero position when it powers up. When using QikEasy Adapter, there is a special feature that allows the user to programmatically force EV3 Gyro to “reset” and recalibrate. To perform this forced “reset”, you only need to turn on the emulated sensor’s light control (even though the physical gyro doesn’t have any light).
- During the “reset” process, the detected Spike Prime Distance Sensor will disappear on the App for 5 to 10 seconds, and then it will reappear. The “wait until” control block is used to detect when the “reset” is finished.
- IMPORTANT: Before the “reset” begins, you should keep the gyro stationary on a flat surface to allow the gyro to properly calibrate itself. You should only touch and move it after the Applause ring tone is played.
- The following Word Block program provides an example of how to perform Gyro reset at the starting of the program. It also demonstrates how to decode the data read from the Gyro.
- The GetAngle&Rate custom block is defined for converting Distance Sensor’s distance data into Angle & Rate, and save them into the variables GyroAngle (ranged from 0 to 360) and GyroRate (ranged from -50 to 50).
- Its main program has a Forever loop that continuously calls the GetAngle&Rate custom block to read from the sensor and to decode the angle and rate values into the global variables GyroAngle and GyroRate. To use this values, one may access these global variables in another event loop.
Main Axis Angle and Rotation Rate:
To access EV3 Gyro data in Python, we will use the LEGO’s advanced hub API. Similar to using Word Blocks, we have to decode Angle and Rate based on the numeric range the incoming data falls in.
Note that the data coming from the sensor range from 0 to 2000, which is 10x bigger than the word block version. The formulas for decoding the incoming data are:
- When SensorValue < 1000:
Angle = SensorValue * 3.6/10 (result in the range of 0 to 360)
- When SensorValue >= 1000:
Rate = SensorValue – 1500 (result in the range of -500 to 500)
In the following example, we show how one would read Angle & Rate in Python. The algorithm of this code is exactly the same as the Word Block version. The only difference is that in Python, most of the numbers involved are 10x bigger than the Word Block ones. This is a good thing as it gives us better resolution for the data. Everything else should be self-explanatory by the comments in the code. Please refer to the explanation for the Word Block version regarding special things to note when running the program.
# On Spike Prime, the first 2 lines should be:
# from spike import PrimeHub
# myHub = PrimeHub()
from mindstorms import MSHub
myHub = MSHub()
# See https://lego.github.io/MINDSTORMS-Robot-Inventor-hub-API/class_device.html for documentation
import hub
from utime import sleep_ms
gyro = hub.port.A.device
# Initialize global variables
GyroAngle = 0 # expected range 0 to 360
GyroRate = 0 # expected range -500 to 500
# Function for converting raw sensor data to user consumable Angle & Rate
def getAngleRate(SensorData):
global GyroAngle, GyroRate
if SensorData < 1000:
GyroAngle = SensorData * 3.6 / 10
else:
GyroRate = SensorData - 1500
print("Starting Gyro calibration. A tone will be played once calibration is complete.")
# Force reset the gyro by turning on top left LED segment @ Mode 5
gyro.mode(5, bytes([1, 0, 0 , 0]))
# Wait till the sensor finish rebooting. Must keep Gyro stationary during this time.
for x in range(100):
gyro.mode(0)
# if gyro is not able to properly get data -> SLEEP and keep trying
if gyro.get(0)== []:
sleep_ms(500)
# The Gyro is now ready for use
myHub.speaker.beep(70, 1)
# Loop to retrieve Angle & Gyro values from sensor
while(1):
sleep_ms(300)
# Get Angle & Rate data from gyro @ Mode 0
getAngleRate( gyro.get(0)[0] )
print("Angle:", GyroAngle, "Rate:", GyroRate)
Gyro Secondary Axis Tilt Angle:
EV3 Tilt Angle and Tilt Rate can only be accessed through Python, and they are only available in newer models of EV3 Gyro sensor. If you try the following program and it doesn’t work, it most likely means you have an older version of the sensor that doesn’t support this feature.
Tilt Angle data is returned in Mode 4 of the emulated Distance Sensor. The data range is from 0 to 360, representing 0 to 360 degrees. No conversion is needed.
Below is an example program that demonstrates how to use Python to read the Tilt Angle data.
# On Spike Prime, the first 2 lines should be:
# from spike import PrimeHub
# myHub = PrimeHub()
from mindstorms import MSHub
myHub = MSHub()
# See https://lego.github.io/MINDSTORMS-Robot-Inventor-hub-API/class_device.html for documentation
import hub
from utime import sleep_ms
gyro = hub.port.A.device
# Initialize global variables
GyroTiltAngle = 0 # expected range 0 to 360
print("Starting Gyro calibration. A tone will be played once calibration is complete.")
# Force reset the gyro by turning on top left LED segment @ Mode 5
gyro.mode(5, bytes([1, 0, 0 , 0]))
# Wait till the sensor finish rebooting. Must keep Gyro stationary during this time.
for x in range(100):
gyro.mode(0)
# if gyro is not able to properly get data -> SLEEP and keep trying
if gyro.get(0) == []:
sleep_ms(500)
# The Gyro is now ready for use
myHub.speaker.beep(70, 1)
# Loop to retrieve Tilt Angle value from sensor
gyro.mode(4)
while (1):
sleep_ms(300)
# Get Tilt Angle data from gyro @ Mode 4
GyroTiltAngle = gyro.get(0)[0]
# Print to console
print("Tilt Angle:", GyroTiltAngle)Gyro Secondary Axis Tilt Rate:
EV3 Tilt Angle and Tilt Rate can only be accessed through Python, and they are only available in newer models of EV3 Gyro sensor. If you try the following program and it doesn’t work, it most likely means you have an older version of the sensor that doesn’t support this feature.
Tilt Rate data is returned in Mode 1 of the emulated Distance Sensor. Its data range is from 0 to 320, representing -500 to 500. Below is the formula that transforms the data range from [0-320] to [-500 – 500]:
Below is an example program that demonstrates how to use Python to read the Tilt Rate data.
# On Spike Prime, the first 2 lines should be:
# from spike import PrimeHub
# myHub = PrimeHub()
from mindstorms import MSHub
myHub = MSHub()
# See https://lego.github.io/MINDSTORMS-Robot-Inventor-hub-API/class_device.html for documentation
import hub
from utime import sleep_ms
gyro = hub.port.A.device
# Initialize global variables
GyroTiltRate = 0 # expected range -500 to 500
# Function for converting raw sensor data to user consumable Tilt Rate
def getTiltRate(SensorData):
global GyroTiltRate
GyroTiltRate = ( SensorData - 160 ) * 25 / 8
print("Starting Gyro calibration. A tone will be played once calibration is complete.")
# Force reset the gyro by turning on top left LED segment @ Mode 5
gyro.mode(5, bytes([1, 0, 0 , 0]))
# Wait till the sensor finish rebooting.Must keep Gyro stationary during this time.
for x in range(100):
gyro.mode(0)
# if gyro is not able to properly get data -> SLEEP and keep trying
if gyro.get(0) == []:
sleep_ms(500)
# The Gyro is now ready for use
myHub.speaker.beep(70, 1)
# Loop to retrieve Tilt Rate value from sensor
gyro.mode(1)
while(1):
sleep_ms(300)
# Get Tilt Rate data from gyro @ Mode 1
getTiltRate( gyro.get(0)[0] )
print("Tilt Rate:", GyroTiltRate)
A Note on Resetting Gyro and Accessing Gyroscopic Data on Multiple axises:
It would have been useful to have the ability to read gyroscopic data on both the Main and Secondary Axis (i.e. the Tilt Angle and Rate) at the same time. However, based on experimentation with EV3 Gyro Sensors, we found that whenever we switch mode, the gyro readings would automatically get reset to zero. This essentially makes it impossible to use the EV3 gyro on multiple axises in the same program. Therefore your only option is to choose which rotational axis data you use well ahead of writing any code for your project. As a policy, accessing main axis angle and tilt angle in the same program is unsupported.
On the topic of resetting gyro to zero, we said previously, in most projects we recommend you to reset the robot’s gyro to zero at program start up. As in the examples above, we recommend using a command like: “gyro.mode(5, bytes([1, 0, 0 , 0]))” to force such reset to happen. This would do a full reboot of the sensor and would trigger the sensor to reconnect to the hub. This whole process will take 5 to 10 seconds.